Imagine the internet is an infinite library filled with billions of books (websites). When someone searches for an answer, they go to the head librarian—Google. In a split second, the librarian scans its entire catalog and recommends the best, most relevant books on the very first shelf.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of making your website the book that the librarian confidently recommends first.
If your site is buried in the back of that library—on the second, third, or tenth page of search results—it’s effectively invisible to 99% of people. This article isn't another boring list of terms. It’s a practical guide to the rules of the game set by search engines, showing you how to step out of the shadows and turn search traffic into real customers.
Chapter 1: Behind the Curtain: How Google Finds Your Site in Under 0.5 Seconds
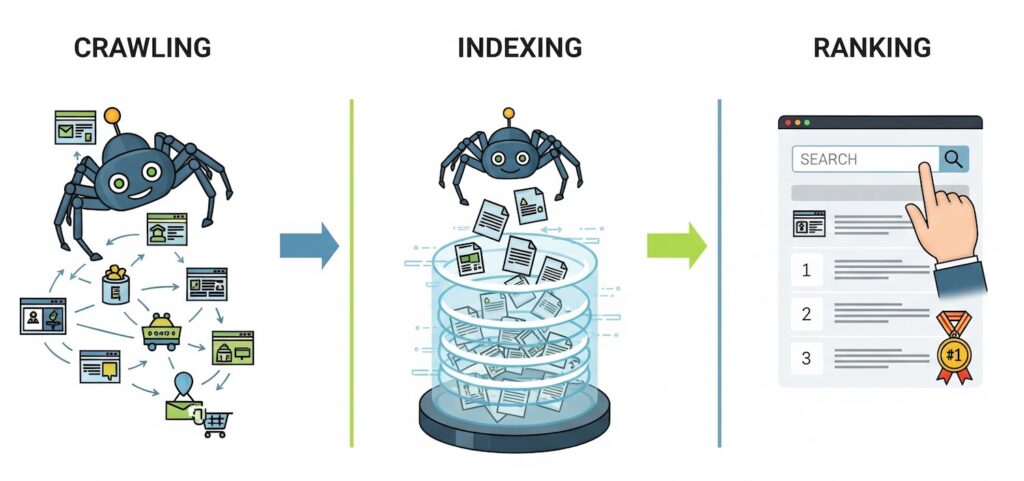
To effectively influence search engines, you have to understand how they think. The entire process, from discovering your site to showing it in search results, breaks down into three key stages.
Step 1: Crawling (Discovery)
Search engines use special robots (often called spiders or crawlers) to scan the internet. Like tireless explorers, they follow links from one page to another, discovering new and updated content 24/7.
- What this means for you: If your site has a confusing structure, broken links, or important pages with no links pointing to them, the robots will simply never find them. Your job is to create a clear “map” for them using a
sitemap.xmlfile and a logical internal linking structure.
Step 2: Indexing (Filing)
After finding a page, a robot analyzes its content: the text, images, videos, and code. This information is then saved and organized in a massive database called the index. Think of indexing as adding a new book to the library's official card catalog.
- What this means for you: Not everything that gets crawled gets indexed. Pages with duplicate, thin, or useless content, or pages blocked by a
robots.txtfile, will be ignored. Your content has to be valuable to earn its spot in the index.
Step 3: Ranking (Recommending)
This is the final act. When a user types in a search query, the search engine scans its index and uses complex algorithms to determine which pages best answer that query. Those pages are then arranged in order of relevance in the search results.
- What this means for you: The algorithms are constantly changing and weigh hundreds of factors, from your site's loading speed to your brand's reputation. SEO is the ongoing work of aligning your website with these quality factors.
Chapter 2: The Three Pillars of SEO: The Foundation of Your Search Success
All SEO work is built on three interconnected pillars. You cannot achieve long-term success by neglecting any one of them.
Pillar #1: Technical SEO (The Foundation of Your House)
This is where you must always start. It’s everything that happens “under the hood” of your site. If your technical foundation is cracked, even the world's best content won't save you.
- Site Speed: In 2025, users won't wait longer than 2-3 seconds for a page to load. A slow site equals a lost customer and a negative signal to Google.
- Mobile-Friendliness: The majority of searches happen on mobile devices. Google now operates on a “mobile-first” basis, meaning it primarily evaluates the mobile version of your site. If it's clunky, your rankings will suffer.
- Security (HTTPS): An SSL certificate is no longer optional. It's a matter of basic digital hygiene and a requirement for building trust with both users and search engines.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): This is a special type of code that helps search engines better understand your content. It’s what enables rich snippets in search results—like star ratings, prices, and event times. This gives you a powerful competitive edge on the results page.
Pillar #2: On-Page SEO (Content Quality and Relevance)
This pillar covers the optimization of everything users and crawlers see directly on your pages. Here, user intent is king.
- Content Quality and E-E-A-T: Forget about mindlessly stuffing your text with keywords. Today, Google evaluates content using a framework called E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Your content must be expertly written, provide a comprehensive answer, and be completely reliable.
- Keywords: Keywords are still crucial, but they are used to understand a topic, not to spam a page. The primary keyword should appear in your main heading (H1), page title, and opening paragraph. Related terms and synonyms should be woven naturally throughout the text.
- Content Structure (H1-H6): A clear hierarchy of headings is the skeleton of your article. An H1 is for the main title, H2s for major sections, and H3s for subsections. This helps both users and robots easily navigate your content.
Pillar #3: Off-Page SEO (Your Digital Reputation)
This pillar includes everything that happens outside of your website to build its authority and reputation.
- Backlinks: This is the cornerstone of off-page SEO. Every link from a reputable, relevant website acts as a vote of confidence. The more high-quality sites that link to you, the more authority you have in Google's eyes. A link from Forbes is worth a thousand times more than a link from an unknown forum.
- Brand Mentions: Even a simple mention of your brand name on other sites, without a hyperlink, is considered a positive signal.
- Social Signals: While social media engagement (likes, shares) isn't a direct ranking factor, it drives traffic, builds brand awareness, and often leads to the natural creation of valuable backlinks.
Chapter 3: SEO Isn't an Expense, It's Your Most Valuable Digital Asset
Many businesses mistakenly view SEO as a marketing expense. This is the wrong way to think about it.
- Long-Term Results: Unlike paid ads (PPC), which stop working the moment you stop paying, the results from SEO are cumulative and long-lasting. A single high-quality article can bring in customers for years to come.
- High Return on Investment (ROI): Organic traffic from search is highly targeted. People are already looking for what you offer. As a result, this traffic typically converts at a higher rate than traffic from most other channels.
- Trust and Credibility: Ranking in the top three organic search results builds immense trust. Users have a subconscious bias: “If Google thinks this is the best result, it must be.”
Your First Step to the Top of the Search Results
SEO can seem complex, but its principles are logical. Start small, but start right:
- Run an Audit: Make sure your site loads quickly and is easy to use on mobile devices.
- Pick One Important Page: Analyze the top 10 competitors for your main target keyword.
- Make It Better: Rewrite and expand your page based on the principles of E-E-A-T. Turn it into the most helpful and comprehensive resource available on that topic.
The world of SEO is always changing, but its foundation—creating value for the user—remains constant. Follow that principle, and the search engines will reward you.













